What is PAM?
Polyacrylamide (abbreviated as PAM) is a polymer with the formula (-CH2CHCONH2-). It has a linear chain structure. PAM is a high molecular weight water-soluble or swellable polymer formed from acrylamide or its derivatives.
PAM is a water-soluble synthetic polymer with useful properties such as good adhesion, proper hygroscopicity, high hydrophilicity and nontoxicity. It is mainly used in water treatment as well as in the paper and mineral industries.
PAM can be used in several forms:
- Powder
- Powder added to water (wet, as a stock solution)
- Emulsion
- Gel blocks or bricks

Applications of PAM
Anionic polyacrylicamide are widely used as thickening agent, binder, super absorbent, soil conditioner, filtering aid, flocculating agent, crosslinker, suspending agent, lubricant, and oil recovery agent. One of its largest uses is waste water treatment. When added to waste water, it causes suspended particles to aggregate and to precipitate. In municipal and industrial waste water treatment it can be used in all liquid-solid separation processes including primary sewage treatment. PAMs are also used to treat water from mineral mining operations. Another common use is oil extraction and recovery. When water is injected into the well, PAM assists in pushing oil locked in reservoirs towards the pump by increasing the viscosity of the injected water.

PAM Production Process
The production process of PAM mainly includes batching, polymerization, granulation, drying, crushing and sieving and packaging.
Acrylamide + water (initiator/polymerization) →polyacrylamide gel → granulation → drying → crushing and screening (Weiliang provides sieving equipment for PAM sieving) → polyacrylamide product

The crushed polyacrylamide is somewhat like crude salt, irregularly granulated and with temperature (50-60°), high viscosity when it meets water. The difficulty of sieving is how to improve the accuracy of the second layer of sieving.
Traditional sieving of polyacrylamide is done by rotary vibrating screen.
But there are the following problems.
- 1. low output;
- 2. low screening precision of the bottom layer;
- 3. easy to block the screen.

IN PURSUIT OF HIGHER OUTPUT & PRECISION, WEILIANG ADOPTS THE TUMBLER SCREEN IN PAM SCREENING
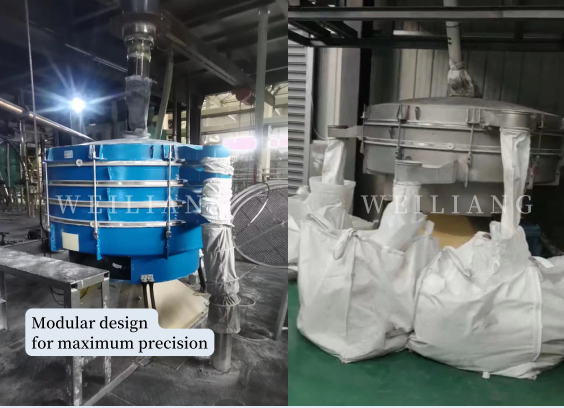

Two layers:Coarse material returns to secondary crushing.
Intermediate material and fine powder are finished products.
Mesh: 16- 80 mesh.
Modular design for maximum precision.
YBS tumbler screen effectively solves the screening problem of PAM
- Larger screening area – increased capacity
- Three-dimensional tumbling motion, modular design – improved sieving precision
- Two different screen cleaning systems – reduced screen blocking
PAM Production Methods
Polyacrylamide production methods are radiationpolymerization, solution polymerization, and emulsion and inverse emulsion polymerization method.
| 1.Radiation-induced method Radiation-induced method acrylamide monomer polymerization initiator direct solid polyacrylamide products or γ- ultraviolet rays. The production process is simple, but the equipment investment and the molecular weight distribution of the resulting product is very wide, so there is no large-scale industrial production. |
| 2. Solution Polymerization Aqueous solution polymerization is the traditional method of production of polyacrylamide, using this method can produce polyacrylamide gels and powder products. General polyacrylamide colloid 8% -10% aqueous solution of acrylamide in the role of initiator directly polymerized; polyacrylamide powder is more polymerized with 25% -30% acrylamide solution, after the polymerization by polyacrylamide colloid granulation, kneading, drying, crushing obtained after product. Wherein the polymerization reaction is a key step. The method has simple production safety, process equipment and low cost of production, etc. |
| 3. Emulsion Polymerization Emulsion polymerization is a conventional operation in the dispersed aqueous acrylamide solution in an organic solvent such as gasoline, with vigorous stirring, the solution was uniformly dispersed emulsion system is formed, followed by the addition of acrylamide initiator reaction of polyacrylamide. Features of this method is the high rate of polymerization conditions at high conversion rate can be high molecular weight products (latex or powder). |
| 4. Inverse Emulsion Polymerization Inverse emulsion polymerization method is a method by means of a water-soluble acrylamide surfactant (use of non-ionic surfactant) the action of acrylamide monomer is dispersed in the oil phase to form the emulsion system, the role of initiator in the emulsion polymerization is carried out to form a stable high molecular weight polyacrylamide instant latex products, after dehydration by azeotropic distillation to obtain a powderypolyacrylamide. The reaction system was stable, easy to control, suitable for the preparation of high molecular weight and a narrow molecular weight distribution latex or polyacrylamide powder products. |
For more information, please feel free to contact us!

