
What is Lignin
Lignin is a complex organic polymer that is a major component of plant cell walls. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose. Lignin fills the spaces in the cell wall matrix between cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin components, providing structural support and rigidity to the plant cell wall.
Functionally, lignin helps plants conduct water efficiently through their tissues and provides strength and resilience to the plant structure. It is particularly important in the vascular tissues of plants, such as wood in trees, where it plays a crucial role in providing mechanical support and aiding in the transport of water and nutrients.
Chemically, lignin is composed of phenylpropane units linked together in a complex three-dimensional network. Its precise composition can vary between different plant species and tissues, contributing to the diversity of properties seen in different types of wood and plant materials.
In industry, lignin has gained attention as a potential source of renewable chemicals and materials. It can be extracted from plant biomass and used in various applications such as adhesives, dispersants, and even as a source of energy through processes like combustion or conversion into biofuels.
Lignin Application
Lignin, as a versatile natural polymer, finds various uses across different industries and applications:
- Wood and Paper Industries
- Pulp and Paper Production: Lignin is a byproduct of the papermaking process when wood fibers are separated to make pulp. It is often burned to generate energy or chemically processed to produce adhesives and additives used in paper manufacturing.
- Wood Adhesives: Lignin-based adhesives can be used in the production of particleboard, plywood, and other wood composites.
- Biofuels and Energy
- Biofuels: Lignin can be converted into liquid biofuels through processes such as pyrolysis and hydrothermal liquefaction.
- Energy Production: Lignin is burned as biomass to generate heat and electricity, contributing to renewable energy sources.
- Chemicals and Materials
- Polymer Additives: Lignin-based compounds can be used as additives to enhance the performance of plastics, resins, and coatings.
- Carbon Fiber Precursors: Lignin can be processed into carbon fibers, which are used in lightweight composites for automotive and aerospace industries.
- Surfactants and Dispersants: Lignin derivatives can act as surfactants and dispersants in various industrial and agricultural applications.
- Environmental Applications
- Soil Amendment: Lignin can be used as a soil conditioner to improve soil structure and nutrient retention.
- Water Treatment: Lignin derivatives are used in wastewater treatment processes as flocculants and adsorbents.
- Pharmaceutical and Health Applications
- Medical: Lignin has potential applications in drug delivery systems and pharmaceutical formulations due to its biocompatibility and ability to encapsulate active ingredients.
- Miscellaneous Uses
- Textiles: Lignin can be used as a dye dispersant and in the finishing of textiles.
- Animal Feed: Lignin can be incorporated into animal feed formulations as a fiber source.
Overall, lignin’s diverse properties and availability make it a valuable resource for sustainable and innovative applications across multiple industries, contributing to the bioeconomy and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
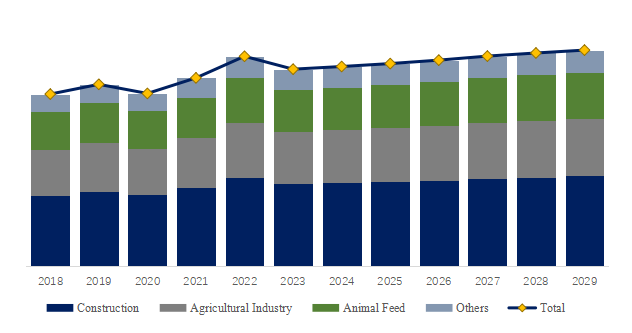
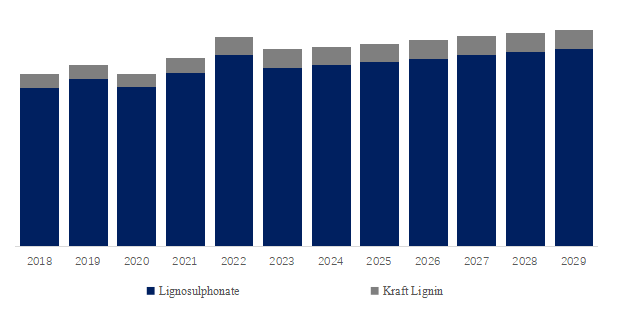
Market Development of Lignin
The lignin industry has been undergoing significant developments and expansions in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of sustainable practices and the search for renewable resources. Here are some key aspects of the lignin market development.
| 1. Shift Towards Bio-Based Products – There is a growing trend towards replacing fossil-based chemicals with renewable alternatives. Lignin, as a natural polymer derived from plant biomass, fits into this trend by offering sustainable sourcing options for various industries. |
| 2. Technological Advancements in Extraction and Processing – Innovations in lignin extraction technologies have improved the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of separating lignin from biomass. Processes such as organosolv, kraft pulping, and enzymatic hydrolysis are being optimized to increase lignin yield and quality. |
| 3. Expansion in Applications – Traditionally used in industries like pulp and paper, lignin’s applications have expanded into sectors such as construction materials (e.g., adhesives, binders for wood products), chemicals (e.g., dispersants, emulsifiers), and energy (e.g., biofuels, biomass for heat and power). |
| 4. Value-Added Products and Derivatives – Lignin derivatives are being developed to enhance their performance in various applications. For instance, lignosulfonates are used as dispersants in concrete admixtures, while lignin-based carbon fibers are being explored for lightweight materials in automotive and aerospace industries. |
| 5. Market Drivers – Environmental regulations promoting sustainable practices and reducing carbon footprint are incentivizing industries to explore lignin-based alternatives. Consumer demand for eco-friendly products and materials is pushing manufacturers to adopt renewable resources like lignin. |
| 6. Regional Market Dynamics – The market for lignin varies regionally based on availability of biomass feed stocks, industrial infrastructure, and regulatory frameworks. Regions with significant forestry or agricultural activities are often prime locations for lignin production. |
| 7. Challenges and Opportunities – Challenges include the variability of lignin properties depending on its source and the need for further research to optimize its performance in different applications. – Opportunities lie in developing novel uses for lignin, such as in advanced materials and high-value chemicals, and in integrating lignin into circular economy models to maximize its value across its lifecycle. |

Lignin Production Process
Lignin can be extracted from biomass using different digestion methods, primarily acid digestion and alkaline digestion. These methods are chosen based on the type of lignin desired and the characteristics of the starting biomass. Here’s an overview of each method:
Acid Digestion Method
- Preparation of Biomass
The biomass (typically wood chips or other lignocellulosic materials) is first prepared by grinding or chipping into small pieces to increase the surface area for digestion.
2. Digestion Process
- Acid Treatment: The prepared biomass is subjected to an acidic environment. Common acids used include sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- The acid breaks down the hemicellulose and cellulose components of the biomass, leaving lignin relatively intact.
- Depending on the process, temperature and pressure conditions may vary but are typically controlled to ensure efficient digestion without excessive degradation of lignin.
3. Lignin Separation
- After digestion, the mixture is typically filtered to separate the dissolved lignin from the remaining solids.
- The filtrate containing lignin is then subjected to further processing steps to recover and purify the lignin.
4. Recovery and Processing
- Neutralization: The acidic solution containing lignin is neutralized to precipitate lignin from the solution.
- Washing and Drying: The precipitated lignin is washed to remove residual acids and impurities. It may then be dried to reduce moisture content.
5. Applications
- Acid-digested lignin can be used in applications requiring higher purity or specific chemical properties, such as in pharmaceuticals or specialty chemicals.

Alkaline Digestion (Kraft Pulping) Method
1. Preparation of Biomass
- Similar to acid digestion, biomass is prepared by grinding or chipping into small pieces.
2. Digestion Process
- Kraft Pulping: The biomass is treated with a mixture of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium sulfide (Na2S) in a digester under high temperature and pressure conditions.
- The alkaline solution breaks down the lignocellulosic structure, dissolving lignin and partially removing hemicellulose and other components.
- The process is typically conducted at temperatures around 160-180°C and pressures of 7-14 bar.
3. Lignin Separation
- After digestion, the resulting mixture (black liquor) contains dissolved lignin, cellulose fibers, and other byproducts.
- Lignin is separated from the black liquor through a series of steps including concentration, acidification, and precipitation.
4. Recovery and Processing
- Precipitation: Lignin is precipitated from the black liquor by acidifying the solution, causing lignin to separate out.
- Washing and Drying: The precipitated lignin is washed and then dried to remove residual chemicals and water.
5. Applications
- Kraft lignin is widely used in industries such as pulp and paper, construction materials (e.g., concrete admixtures), and as a precursor for producing chemicals and bio-based materials.

Comparison and Considerations:
- Chemical Composition: Acid-digested lignin tends to have higher purity and can be more suitable for high-value applications requiring specific chemical properties.
- Industrial Applications: Kraft lignin, due to its production scale and versatility, is more commonly used in large-scale applications such as pulp and paper, where it is recovered as a byproduct of the pulping process.
- Environmental Impact: Both methods have environmental considerations; however, advancements in technology aim to minimize chemical usage and increase efficiency in lignin extraction.
These methods illustrate the versatility of lignin extraction, catering to various industrial needs while contributing to sustainable practices through the utilization of biomass resources.
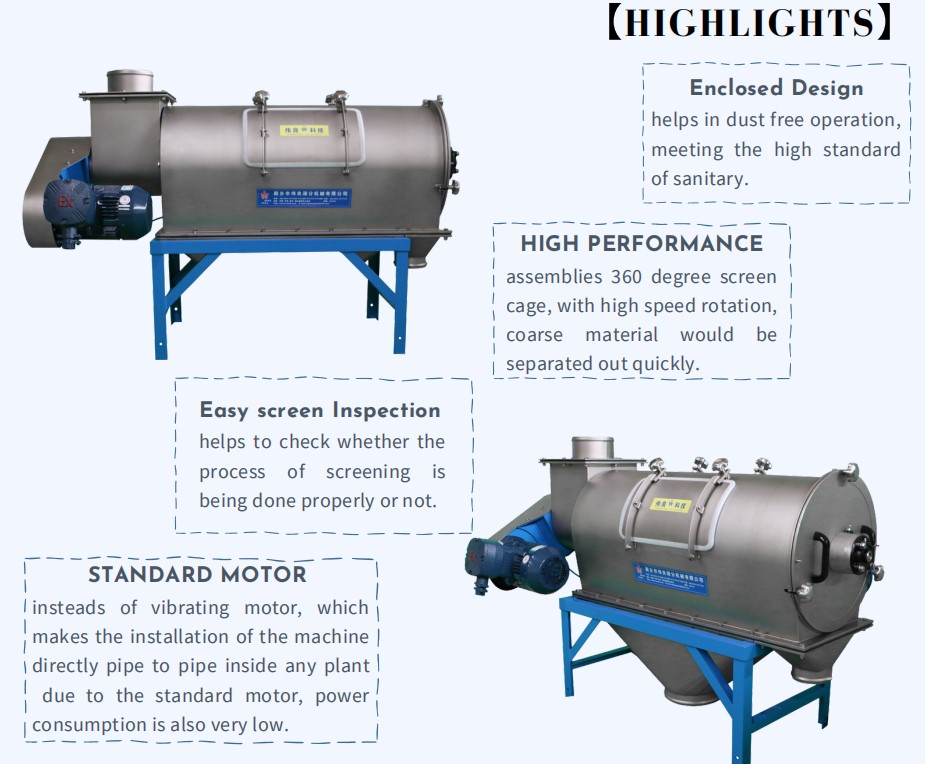
Dry Lignin Powders Sieving – WEILIANG WLQ CENTRIFUGAL SCREEN
A horizontal centrifugal screen is a type of industrial equipment for the separation and classification of materials based on particle size.
1. Centrifugal Force Application
– The screen operates on the principle of centrifugal force, where a cylindrical screen basket rotates horizontally at high speed.
– This rotation creates centrifugal force that pushes particles outward against the screen basket.
2. Particle Separation
– Feed material is introduced into the screen basket, typically through an inlet.
– As the basket rotates, particles smaller than the screen openings pass through the screen, while larger particles are retained and discharged at the end of the screen.
3. Screen Basket Design
– The screen basket is cylindrical and perforated with openings of varying sizes, depending on the desired separation efficiency and particle size distribution.
– The centrifugal force ensures efficient separation of particles, even for materials with high viscosity or high fiber content.
4. Advantages
– High Efficiency: Provides efficient separation of particles based on size, improving product quality.
– Continuous Operation: Can handle large volumes of material continuously, suitable for industrial-scale operations.
– Low Maintenance; Designed for durability and minimal maintenance requirements.
In summary, a horizontal centrifugal screen is a specialized piece of equipment used in various industries for effective particle size separation through the application of centrifugal force. Its design and operation contribute to efficient processing and improved product quality in industrial applications.
WEILIANG WLQ centrifugal screen: versatile and efficient solution for separating, refining, and removing impurities from lighter materials across various industries.
Contact us for your exclusive customized screening solution.
